“`html
Essential Guide to Keto Enol Tautomerism
Understanding Keto Enol Tautomerism
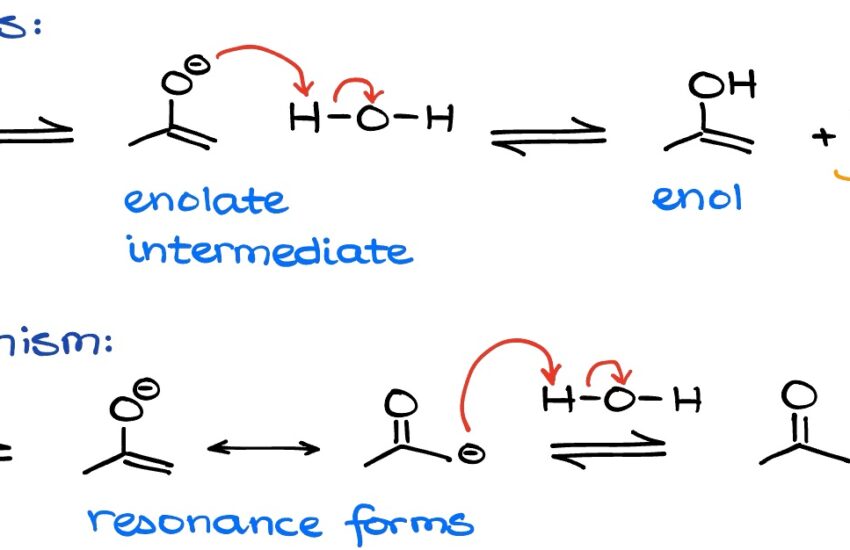
Keto enol tautomerism is a fascinating and crucial concept in **organic chemistry** that involves the interconversion between the keto form and the enol form of a compound. The keto form, typically characterized by a carbonyl group (C=O), is often more stable than its enol counterpart, which contains a double bond between a carbon and an alcohol (C=C-OH). This **tautomeric shift** represents a dynamic equilibrium, where the balance between these two forms can shift based on various reaction conditions and molecular structures. In organic synthesis, understanding this equilibrium and **keto-enol interconversion** is essential for many reaction mechanisms and product outcomes.
Properties of the Keto and Enol Forms
The properties of the keto and enol forms highlight the **stability of the keto form** and the unique characteristics of the enol form. Generally, the keto form is favored due to the resonance stabilization provided by the carbonyl group. However, enols can exhibit intriguing reactivity patterns, particularly due to their ability to participate in **hydrogen bonding** and form **intramolecular interactions**. This unique property allows enols to be crucial in specific chemical transformations such as **aldol condensation** reactions and hydration reactions. Interestingly, the **stability of enol form** is increased in certain structural environments, especially when driven by **intramolecular hydrogen bonding** that stabilizes the enolic configuration.
Keto-Enol Ratio in Reactions
The **keto-enol ratio** is a vital factor when discussing the prevalence of one tautomer over the other in a given reaction. This ratio is influenced by factors such as temperature, solvent effects, and the presence of acidic or basic catalysts. For instance, higher temperatures may favor the kinetic stability of the enol form, especially in specific reaction pathways. Additionally, the choice of solvents can also have a significant impact, since polar protic solvents may stabilize the enol form more effectively than the keto form. Understanding these ratios is integral for chemists when designing synthetic pathways that require specific **keto-enol transformations**.
Significance in Drug Design and Biology
The implications of keto enol tautomerism stretch beyond laboratory studies; it significantly intersects with **drug metabolism** and biological processes. Tautomerization can affect biological activity and reactivity in pharmaceutical compounds. For example, some drugs switch between tautomers within the physiological pH range, ultimately affecting their interactions with biological targets. This has major implications for developing drugs with desired stability and activity. Furthermore, the significance of **keto-enol tautomerization in biology** is illustrated in how certain enzymes and receptors operate, which deeply impacts drug design and therapeutic efficacy.
Mechanisms and Factors Influencing Tautomerization
A proper understanding of the mechanisms behind **keto-enol tautomerization** is pivotal for chemists. The transformation is often catalyzed through acid or base attacks—termed **acid-base catalysis**—affecting the relative amounts of each tautomer present at equilibrium. **Kinetic vs thermodynamic factors** also plays a crucial role here; while kinetic stability might favor the formation of enols under certain conditions, thermodynamic factors emphasize the longevity of the keto form. This duality of **reaction dynamics** in tautomerization makes it a rich field for study, offering insights into how diverse reaction pathways can yield different tautomers based on environmental variables.
Molecular Interactions During Tautomerization
Numerous molecular interactions significantly influence the tautomerization process. **Hydrogen bonds**, both intermolecular and intramolecular, can facilitate or hinder the interconversion between keto and enol forms. For instance, in cases where hydrogen bonding occurs within a cyclic structure or when functional groups participate in stabilization patterns, the enol form can become remarkably stable. **Stereochemistry** also comes into play, influencing how tautomers align and react with various substrates and reagents, ultimately affecting the reaction rates and mechanistic pathways of interconversions.
Catalysts in Tautomerization Reactions
Catalysts are critical in enhancing the reaction rates for keto-enol tautomerization processes. Acid or base catalysts often simplify the transition states involved during these conversions. Understanding how different catalysts influence the **kinetic stability** of the tautomers provides insights into developing more efficient synthetic methodologies. For instance, studies using **NMR and UV-Vis spectroscopy** can monitor tautomerization in real-time, providing valuable data on how catalysts modify reaction pathways, ultimately improving yields and selectivity in chemical reactions involving keto and enol forms.
Impact of pH and Solvent Effects
The influence of pH on **keto-enol tautomerism** cannot be overstated. Variations in acidity can significantly shift the equilibrium between the keto and enol forms, making pH a vital parameter for many organic reactions. Similarly, solvent polarity and protic or aprotic characteristics influence the **reactivity of enols** versus ketones. For instance, a polar protic solvent might stabilize an enol via solvation while simultaneously facilitating the tautomerization process, highlighting the defining impact that solvent selection has on reaction outcomes.
Advanced Analytical Techniques in Studying Tautomerism
Recent advancements in analytical techniques have further elucidated the mechanisms and implications of **keto-enol tautomerization**. Techniques such as NMR spectroscopy have become instrumental for analyzing tautomer distributions in various compounds. This data aids chemists in establishing **equilibrium constants** for keto-enol conversions, enhancing the understanding of how tautomeric ratios evolve under different reaction conditions. Additionally, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry have provided capabilities for the concise separation and identification of **tautomeric forms**, thereby allowing precise examinations of their behavior in various environments.
Computational Methods in Tautomerism
Computational studies provide theoretical insights into the behavior and interactions of tautomers, allowing chemists to predict the stability and reactivity of keto and enol forms with enhanced accuracy. Quantum mechanical calculations can offer a predictive framework for understanding **thermodynamic versus kinetic control** in tautomeric equilibria. These methods allow for the modeling of reaction pathways, enabling researchers to propose mechanistic studies that can affirm experimental findings and broaden the scope of *synthetic pathways* in organic chemistry.
Case Studies Illustrating Keto-Enol Transformations
Several noteworthy examples of **keto-enol transformations in nature** illustrate their profound relevance in chemical systems. One such example is the behavior of 2-pentanone, where acidity and solvent influence the ratio of its tautomeric forms. Analyzing these cases can reveal a comprehensive understanding of how tautomerism shapes reactivity and stability across a range of **biological and organic systems**. Additionally, examining specific compounds and their tautomeric equilibria can unveil their promising applications in drug discovery and material sciences.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding **keto enol tautomerism** is essential for designing organic reactions and synthetic pathways.
- The **keto-enol ratio** is influenced by various factors including pH, solvent effects, and temperature.
- **Analytical techniques** such as NMR and UV-Vis spectroscopy are vital for studying tautomer distributions and mechanistic behavior.
- **Catalytic processes** significantly impact the reaction rates and pathways of tautomerization.
- Advancements in **computational methods** contribute to theoretical predictions and a deeper understanding of tautomer equilibria.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between keto and enol forms?
The main difference between keto and enol forms lies in their molecular structure. The keto form features a carbonyl group (C=O), which grants it **thermodynamic stability**, while the enol form contains a hydroxyl group attached to a double bond, making it reactive under certain conditions. This structural contrast significantly influences their respective stability and reactivity in various chemical scenarios.
2. How can pH influence the keto-enol ratio?
pH has a substantial impact on the keto-enol ratio by influencing the state of protonation or deprotonation of the reactants involved. In acidic conditions, the formation of the enol form can be favored due to the availability of protons, while a basic environment commonly stabilizes the keto form. Thus, adjustments in pH can lead to significant shifts in the equilibrium of these tautomeric forms.
3. Why are advanced analytical techniques important in studying tautomerism?
Advanced analytical techniques are crucial in studying tautomerism as they allow for the precise identification and measurement of **tautomer distributions**. Utilizing technologies such as NMR and chromatography enables chemists to gather data on the equilibrium constants and kinetic behavior of these compounds under various conditions, improving our understanding of reaction mechanisms and enhancing synthetic strategies.
4. What role does intramolecular hydrogen bonding play in the stability of enols?
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding can significantly enhance the **stability of enol forms** by reducing the energy barrier associated with their formation. This definition allows enol configurations to be favored in certain molecular structures, particularly when the rigid arrangement of atoms permits such bonding interactions, ultimately influencing reaction patterns and products in tautomerization.
5. Can you explain the significance of keto-enol tautomerism in pharmaceuticals?
Keto-enol tautomerism is vital in pharmaceuticals as the variations in tautomeric forms can affect a drug’s metabolism, binding affinity, and overall efficacy. Many pharmaceutical compounds exist predominantly as one tautomer, but their alternate forms may exhibit selective receptor binding or reactivity, making understanding this dynamic crucial in drug design and therapeutic applications.
6. What is tautomerization and why is it significant in organic synthesis?
Tautomerization is the process of converting a tautomer into another through a temporary shift in molecular structure. This equilibration is significant in **organic synthesis** because it can directly influence product distribution, reaction rates, and yields. Understanding tautomerization allows chemists to optimize conditions to favor desired products and infer the reactivity patterns of various compounds.
7. How are computational studies enhancing our understanding of keto-enol tautomerism?
Computational studies are enhancing our understanding of keto-enol tautomerism by providing theoretical insights into the kinetics, thermodynamics, and reaction pathways involved in these interconversions. Using quantum mechanics and molecular modeling, researchers can predict how changes in structure or reaction conditions affect tautomeric behavior, ultimately improving experimental outcomes and synthetic methodology.
“`